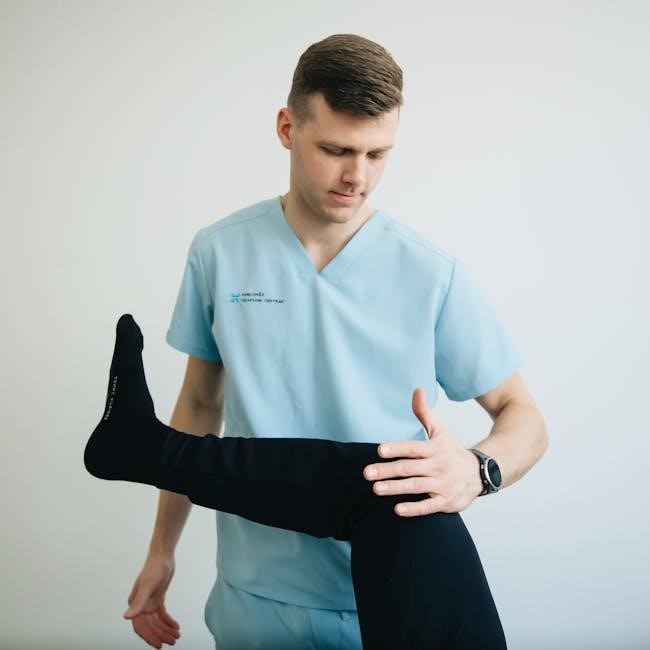
Lower extremity strengthening exercises are essential for improving mobility and preventing injuries. They target muscles in the legs, hips, and ankles, aiding in rehabilitation and enhancing overall stability. These exercises often include activities like towel scrunches and Theraband workouts, complemented by stretches for comprehensive lower limb health.
1.1 Importance of Lower Extremity Strength
Lower extremity strength is crucial for overall mobility, stability, and injury prevention. Strong legs, hips, and ankles support daily activities, enhance athletic performance, and reduce the risk of chronic conditions. Strengthening these muscles improves balance, coordination, and joint health, while also aiding in rehabilitation and preventing injuries. It is essential for maintaining independence and quality of life, particularly as individuals age or recover from injuries.
1.2 Targeted Muscle Groups
Lower extremity strengthening exercises focus on key muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, and hip muscles. These muscles are essential for movement, stability, and balance. The quadriceps and hamstrings support knee function, while the calves and Achilles tendon contribute to ankle mobility. Strengthening the hip muscles, such as the glutes, improves pelvic stability and overall lower limb function. Targeting these groups ensures comprehensive strength and mobility for daily activities, sports, and rehabilitation.
1.3 Benefits for Overall Mobility and Stability
Strengthening the lower extremities enhances mobility and stability by improving muscle function and joint health. Stronger muscles in the legs and hips reduce the risk of injuries and support daily activities like walking and climbing stairs. These exercises also promote better balance and proprioception, which are crucial for maintaining independence and preventing falls. Additionally, enhanced lower limb strength contributes to overall physical function, making it easier to engage in recreational activities and maintain an active lifestyle.

Anatomical Terms and Terminology
Understanding key anatomical terms like flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction is crucial. These terms describe movements and muscle actions in the lower extremities, aiding in precise exercise execution.
2.1 Key Muscles in the Lower Extremities
The lower extremities include key muscles such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. These muscles are essential for movement, stability, and balance. The quadriceps, located in the front of the thigh, facilitate knee extension, while the hamstrings at the back enable flexion. The glutes and hip flexors control hip movement, and the calves, including the gastrocnemius and soleus, are vital for ankle mobility. Understanding these muscles is crucial for effective strengthening exercises and rehabilitation programs targeting the lower limbs.
2.2 Joint Movements and Ranges of Motion
Joint movements in the lower extremities include flexion, extension, and rotation. The hips, knees, and ankles have specific ranges of motion essential for functional activities. For example, the knee typically flexes up to 135 degrees and extends to 0 degrees, while the ankle allows dorsiflexion (20 degrees) and plantarflexion (50 degrees). Understanding these movements is critical for designing effective strengthening exercises and ensuring proper rehabilitation, as limitations in range of motion can hinder mobility and increase injury risk.
2.3 Anatomical Planes of Movement
The lower extremities move within three anatomical planes: sagittal, frontal, and transverse. The sagittal plane involves flexion and extension, such as knee bends. The frontal plane includes abduction and adduction, like hip side lifts. The transverse plane focuses on rotational movements, such as pivoting on one leg. Understanding these planes helps in designing exercises that target specific muscle groups and improve functional movement patterns, ensuring comprehensive lower limb strengthening and proper alignment during rehabilitation exercises.

Benefits of Lower Extremity Strengthening
Strengthening the lower extremities enhances stability, mobility, and muscle function, aiding in injury prevention, rehabilitation, and improving overall physical performance and daily activity efficiency.
3.1 Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation
Strengthening the lower extremities is crucial for preventing injuries and aiding in rehabilitation. Targeted exercises, such as towel scrunches and Theraband workouts, improve muscle function and stability, reducing the risk of harm. For individuals recovering from injuries, these exercises enhance mobility and strength, promoting faster recovery. They also play a key role in rehabilitation programs, helping to restore muscle balance and reduce pain, particularly in the ankles, knees, and hips. Regular practice can significantly accelerate the healing process and prevent future injuries.
3.2 Improved Athletic Performance
Lower extremity strengthening exercises significantly enhance athletic performance by improving power, speed, and endurance. Stronger leg and hip muscles enable better acceleration and deceleration, crucial for sports. Exercises like towel scrunches and Theraband workouts boost stability and coordination, reducing fatigue during prolonged activities. Enhanced muscle function also improves jumping and sprinting abilities, giving athletes a competitive edge. Regular strengthening routines help maintain optimal physical conditioning, ensuring peak performance in various athletic endeavors;
3.3 Enhanced Mobility for Daily Activities
Lower extremity strengthening exercises enhance mobility for daily activities by improving muscle function and joint stability. Stronger legs, hips, and ankles make walking, climbing stairs, and maintaining balance easier. These exercises, such as towel scrunches and Theraband workouts, also improve coordination and reduce fatigue during everyday tasks. Enhanced mobility benefits individuals with limited movement, helping them perform routine activities with greater ease and independence. Regular strengthening routines promote long-term physical function and overall quality of life.
3.4 Strengthening Muscle Balance
Strengthening muscle balance in the lower extremities ensures equal strength around joints, preventing overuse injuries and improving overall stability. Exercises like towel scrunches and Theraband workouts target specific muscle groups, enhancing coordination and movement efficiency. By addressing imbalances between muscles such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, these exercises promote proper alignment and joint mechanics. Improved muscle balance reduces injury risk and enhances athletic performance, while also supporting daily activities with better movement patterns and reduced fatigue.
3.5 Management of Chronic Conditions
Lower extremity strengthening exercises play a crucial role in managing chronic conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and obesity. These exercises improve joint health, reduce pain, and enhance mobility, particularly in individuals with limited physical activity. Strengthening the muscles around the knees, hips, and ankles can alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis and support weight management. For those with diabetes, improved circulation and muscle function aid in overall health. Regular exercise routines also help mitigate the progression of chronic diseases, promoting long-term independence and quality of life.
Types of Lower Extremity Strengthening Exercises
Lower extremity strengthening exercises include isometric, isotonic, and plyometric workouts, as well as balance and proprioception training. These exercises enhance muscle strength, stability, and functional mobility effectively.
4.1 Isometric Exercises
Isometric exercises involve contracting muscles without joint movement, making them ideal for strengthening lower extremities. Examples include wall sits, glute bridges, and quadriceps sets. These exercises improve muscle endurance and strength, particularly beneficial for rehabilitation and injury prevention. They are low-impact, reducing stress on joints, and can be performed anywhere without equipment. Isometric holds, like heel raises, enhance stability and balance. They are especially useful for individuals with mobility limitations, providing a safe and effective way to build lower limb strength and promote functional recovery.
4.2 Isotonic Exercises
Isotonic exercises involve muscle contractions with joint movement, promoting strength and flexibility. Examples include leg extensions, step-ups, and leg presses. These exercises enhance joint mobility and muscle balance, crucial for functional movements. They can be performed with weights, resistance bands, or machines, making them versatile for different fitness levels. Isotonic exercises help improve power and endurance, benefiting both athletes and individuals in rehabilitation. Regular practice can lead to better muscle coordination and overall lower limb function, supporting daily activities and athletic performance effectively.
4.3 Plyometric Exercises
Plyometric exercises are high-intensity movements that focus on explosive power and speed. Common examples include jump squats, box jumps, and calf raises. These exercises enhance muscle reactivity and neuromuscular coordination, making them ideal for athletes seeking to improve performance. Plyometrics also boost muscle fiber activation and temporary joint stiffness, optimizing energy transfer for explosive movements. Regular practice can improve power, agility, and overall lower limb function, making them a valuable addition to strengthening routines for both sports and rehabilitation purposes.
4.4 Balance and Proprioception Training
Balance and proprioception training focuses on improving stability and body awareness. These exercises, such as single-leg stands, wobble board work, and heel-to-toe walking, enhance neuromuscular communication. They strengthen the connection between muscles, joints, and the brain, reducing injury risk and improving coordination. Balance training is particularly beneficial for rehabilitation, as it restores functional stability and confidence in daily activities and sports. Incorporating proprioceptive drills, like BOSU ball exercises, further refines lower extremity control and overall physical performance.

Strengthening Exercises for Specific Muscle Groups
Strengthening exercises target specific muscle groups like quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, and hips. These exercises enhance lower extremity strength, improve joint stability, and support overall mobility. Resistance bands, bodyweight, and specialized equipment are often used to focus on individual muscle groups, ensuring balanced development and injury prevention. Proper technique and progression are key to maximizing results and maintaining muscle health.
5.1 Quadriceps Strengthening Exercises
Quadriceps strengthening exercises focus on the muscles in the front of the thigh, essential for knee stability and mobility. Common exercises include leg extensions, step-ups, and wall sits. Resistance bands or bodyweight can be used to enhance resistance. These exercises improve strength, reduce injury risk, and support daily activities like walking and climbing stairs. Progressing gradually and maintaining proper form are crucial to avoid strain. Incorporating variations, such as single-leg extensions, can target specific areas for balanced development.
5.2 Hamstring Strengthening Exercises
Hamstring strengthening exercises target the muscles at the back of the thigh, crucial for knee and hip function. Key exercises include deadlifts, leg curls, and glute-ham raises. These can be performed with bodyweight or resistance, such as dumbbells or machines. Proper form and gradual progression are vital to avoid injury. Incorporating stretches post-exercise enhances flexibility and reduces muscle soreness. Strengthening hamstrings improves athletic performance, prevents injuries, and supports daily activities like running and climbing.
5.3 Calf and Achilles Tendon Strengthening
Calf and Achilles tendon strengthening exercises focus on improving the muscles and tendons in the lower leg. Key exercises include heel raises, calf presses, and towel scrunches. These activities enhance ankle stability, reduce injury risk, and improve mobility. Strengthening the calf muscles and Achilles tendon supports daily activities, sports performance, and overall lower limb health. Consistent practice helps prevent conditions like Achilles tendinitis and promotes faster recovery for individuals with existing injuries or chronic pain.
5.4 Hip and Glute Strengthening Exercises
Hip and glute strengthening exercises are crucial for enhancing stability and power in the lower extremities. Key exercises include squats, lunges, glute bridges, and clamshells, which target the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus muscles. These exercises improve hip mobility, reduce injury risk, and enhance athletic performance. Strengthening the hips and glutes also supports proper posture, balances muscle groups, and boosts overall lower limb functionality, making them essential for both rehabilitation and fitness routines.

Stretching Exercises to Complement Strengthening
Stretching is vital to enhance flexibility and reduce muscle tension after strengthening exercises. Focus on hamstrings, hip flexors, calves, and Achilles tendon for optimal lower extremity mobility.
6.1 Hamstring and Hip Flexor Stretches
Hamstring and hip flexor stretches are crucial for improving flexibility and reducing muscle tension. Seated hamstring stretches and standing hip flexor stretches are effective. These exercises enhance range of motion, prevent tightness, and reduce injury risk. Incorporate these stretches post-strengthening to promote recovery and maintain muscle balance. Hold each stretch for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply, and avoid bouncing. Regular stretching complements strengthening by ensuring optimal muscle function and mobility in the lower extremities. Proper technique is essential to maximize benefits and avoid discomfort.
6.2 Calf and Achilles Tendon Stretches
Calf and Achilles tendon stretches are vital for maintaining ankle mobility and preventing tightness. Standing calf stretches and seated Achilles stretches are commonly recommended. These exercises target the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, improving flexibility and reducing injury risk. Perform stretches slowly, holding for 20-30 seconds, and repeat 2-3 times. Proper technique ensures effectiveness and safety. Regular stretching complements strengthening by enhancing muscle length and promoting recovery. Incorporate these stretches after strengthening exercises to maintain optimal lower extremity function and mobility.
6.3 Quad and IT Band Stretches
Quad and IT band stretches improve flexibility and reduce tightness in the thigh muscles. Standing quad stretches involve pulling the foot toward the buttocks, targeting the quadriceps. For the IT band, side-lying stretches or leg lifts can be effective. These exercises enhance mobility and reduce injury risk, particularly for runners and athletes. Perform stretches slowly, holding for 20-30 seconds, and repeat 2-3 times. Regular stretching complements strengthening by improving muscle length and promoting recovery. Incorporate these stretches after strengthening exercises to maintain optimal lower extremity function and balance.

Progression of Strengthening Exercises
Progression involves advancing from basic to more challenging exercises, adjusting resistance, and increasing intensity as strength improves, ensuring continued growth and alignment with individual goals.
7.1 Beginner-Level Exercises
Beginner-level exercises focus on building foundational strength and stability in the lower extremities. They often include bodyweight exercises like ankle pumps, toe raises, and seated leg extensions. These movements help improve muscle activation and joint mobility without requiring advanced equipment. Towel scrunches and Theraband exercises are also common, targeting the feet and ankles. Progression is gradual, ensuring proper form and minimizing injury risk. These exercises are ideal for those starting rehabilitation or new to strengthening programs.
7.2 Intermediate-Level Exercises
Intermediate-level exercises build on foundational strength by introducing resistance and complexity. Activities like resistance band workouts, step-ups, and single-leg balancing are common. These exercises enhance muscle balance, joint stability, and functional movement patterns. They are suitable for individuals who have mastered beginner exercises and are ready to progress. Incorporating dynamic movements and increased intensity helps improve overall lower extremity function and prepares for more advanced training.
7.3 Advanced-Level Exercises
Advanced-level exercises are designed for individuals with significant strength and stability. They include plyometric movements, dynamic balancing, and high-resistance training. Activities like box jumps, lateral bounds, and single-leg hops challenge power and coordination. These exercises aim to enhance explosive strength, agility, and functional performance. Advanced routines often incorporate complex movement patterns and equipment like balance boards or heavy resistance bands. Progressing to this level requires mastery of intermediate exercises and focuses on optimizing lower extremity function for high-demand activities.
Safety and Precautions
Proper warm-up, technique, and equipment are crucial. Avoid overtraining to prevent injury. Use tools like Theraband correctly and consider professional guidance for safe exercise execution.
8.1 Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
A proper warm-up and cool-down are essential for safe lower extremity strengthening. Begin with dynamic stretches, such as leg swings and ankle circles, followed by light cardio like walking. After exercise, cool down with static stretches for hamstrings, hip flexors, and calves. Incorporate foam rolling to release muscle tension and improve circulation. These routines help prevent injuries, reduce muscle soreness, and enhance recovery. Consistency in these practices ensures optimal results and maintains overall lower limb health during strengthening programs.
8.2 Avoiding Overtraining and Injury
To prevent overtraining and injury, listen to your body and avoid excessive strain. Incorporate rest days and monitor progress to ensure muscles recover. Use the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) for minor injuries. Focus on proper form and technique during exercises to minimize risk. Gradually increase intensity and avoid overloading joints. Prioritize quality over quantity to maintain long-term lower extremity health and avoid setbacks. Consulting a professional for personalized guidance can also help prevent injuries and ensure safe progression in strengthening programs.
8.4 Proper Equipment and Technique
Using proper equipment and technique is crucial for effective and safe lower extremity strengthening. Essential tools include resistance bands, ankle weights, and balance boards. Theraband exercises are popular for controlled resistance. Ensure equipment is clean and well-maintained. Focus on maintaining proper form to target the correct muscles. Avoid using heavy weights that compromise technique. Use slow, controlled movements to maximize effectiveness. Consulting a professional can help tailor exercises to individual needs, ensuring safety and optimal results. Proper technique prevents injury and enhances the benefits of strengthening programs.
Sample Workout Routine
A sample workout routine includes warm-up stretches, towel scrunches, calf raises, and Theraband exercises. Perform 3 times weekly for 30-45 minutes, focusing on controlled movements.
9.1 Weekly Exercise Plan
A well-structured weekly exercise plan for lower extremity strengthening includes 3-4 days of targeted workouts. Day 1: Focus on ankle and calf exercises like towel scrunches and calf raises (3 sets of 15 reps). Day 2: Strengthen hips and quads with side-lying leg lifts and wall sits (3 sets of 15 reps). Day 3: Emphasize hamstrings and glutes with bridges and step-ups (3 sets of 15 reps). Day 4: Rest or active recovery with light stretching and foam rolling. Incorporate balance training on alternate days for stability.
9.2 Exercise Frequency and Duration
Engage in lower extremity strengthening exercises 3-4 times weekly for optimal progress. Each session should last 30-45 minutes, including a 5-10 minute warm-up. Start with 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions per exercise and gradually increase intensity. Allow 48-72 hours of rest between sessions targeting the same muscle groups. Consistency is key for muscle adaptation and strength improvement. Incorporate dynamic stretches during warm-ups and cool-downs to enhance flexibility and reduce injury risk.
9.3 Incorporating Rest Days
Rest days are crucial for muscle recovery and strength gains. Include 1-2 rest days weekly to allow your lower extremities to heal and adapt. Overtraining can lead to injury or fatigue. Use rest days for light activities like walking or stretching to maintain mobility without strain. Ensure rest days complement your exercise routine, promoting long-term progress and preventing burnout. Proper recovery enhances the effectiveness of your strengthening exercises and supports overall muscle balance and stability.
Resources and References
Find detailed guides in “Lower Extremity Physical Therapy Exercises PDF,” which includes stretches and strengthening exercises for comprehensive rehabilitation. Explore the “LOWER-LIMB FOLLOW-UP” system for structured routines and progress tracking, ideal for both therapists and individuals. Additionally, research studies on strengthening exercises for specific populations, such as pregnant women and children with arthritis, provide evidence-based approaches for tailored programs.
10.1 PDF Guides and Worksheets
Downloadable PDF guides provide comprehensive outlines for lower extremity strengthening exercises, including detailed stretches, Theraband workouts, and progress tracking sheets. These resources often feature step-by-step instructions and anatomical illustrations to ensure proper form. The “LOWER-LIMB FOLLOW-UP” system offers structured routines, while studies on specific populations, such as pregnant women and children with arthritis, provide evidence-based exercise plans. These PDFs are ideal for therapists, patients, and individuals seeking personalized rehabilitation or strengthening programs.
10.2 Recommended Reading Materials
Recommended reading materials on lower extremity strengthening exercises include academic journals, clinical studies, and therapy guides. These resources provide evidence-based insights into exercise efficacy, particularly for populations like hospitalized pregnant women and children with arthritis. Renew Physical Therapy and the “LOWER-LIMB FOLLOW-UP” system offer detailed exercise programs. Additionally, studies on obesity-related joint health and hamstring injury rehabilitation are valuable for understanding the importance of strengthening exercises in various conditions. These materials are essential for therapists, researchers, and individuals seeking in-depth knowledge.
10.3 Online Tools and Apps
Online tools and apps like the “LOWER-LIMB FOLLOW-UP” system provide interactive platforms for lower extremity strengthening exercises. These resources include goal-oriented modules, video demonstrations, and progress tracking features. Apps offer customizable exercise plans, reminders, and virtual coaching to enhance adherence. Many platforms cater to specific needs, such as rehabilitation or sports performance, making them accessible for diverse user groups. These digital tools complement PDF guides, offering a modern approach to strengthening exercises and promoting consistent practice for optimal results.